NexGen Smart Buildings
- Mark Lafond, RA
- Mar 2, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Mar 16, 2024
Merging Building Management Systems, Robotics, Artifical Intelligence, IoT and Blockchain Technologies

As architects and urban planners continue to grapple with the challenges of energy and urban resilience, the integration of advanced smart building technologies becomes increasingly paramount. These technologies not only enhance the efficiency and sustainability of buildings but also contribute to the overall resilience of urban environments.
One key area of innovation in smart building technology is the development of intelligent energy management systems. These systems leverage real-time data and predictive analytics to optimize energy usage, reduce waste, and maximize the performance of renewable energy sources. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns of energy consumption and adjust heating, cooling, and lighting systems accordingly to minimize energy expenditure while maintaining occupant comfort.
Another promising technology is the use of building-integrated renewable energy systems, such as solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heat pumps. These systems enable buildings to generate their own clean energy on-site, reducing dependence on external power grids and mitigating the impact of power outages.
Moreover, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and hydrogen fuel cells, allow buildings to store excess energy for later use, further enhancing their resilience and autonomy.
In addition to energy management, smart building technologies also encompass a wide range of innovations aimed at improving occupant health, comfort, and productivity. For instance, sensor-based systems can monitor indoor air quality, temperature, humidity, and lighting levels, automatically adjusting environmental conditions to create a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
Furthermore, smart building automation systems enable remote monitoring and control of building systems, allowing facility managers to identify and address issues proactively, optimize maintenance schedules, and minimize downtime.
Emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing the way buildings are designed, constructed, and operated. IoT sensors embedded in building components and infrastructure can provide real-time feedback on performance, detect anomalies, and facilitate predictive maintenance. Cloud-based platforms enable centralized data management and analysis, allowing building operators to gain insights into energy usage patterns, identify opportunities for optimization, and make data-driven decisions.
Moreover, AI-powered building management systems can analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources to identify trends, predict future energy demand, and optimize building operations in real-time. For example, AI algorithms can dynamically adjust lighting levels based on occupancy patterns, optimize HVAC settings to minimize energy consumption, and even predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Beyond individual buildings, smart city initiatives seek to leverage interconnected technologies to create more efficient, resilient, and sustainable urban environments. By integrating smart buildings with smart grids, smart transportation systems, and other infrastructure, cities can optimize resource allocation, reduce environmental impact, and enhance quality of life for residents. For example, smart grid technologies enable bidirectional energy flows between buildings and the electrical grid, allowing excess energy generated by buildings to be fed back into the grid and distributed to other users.
Smart building technologies play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of energy, urbanization, and resilience. By leveraging advanced energy management systems, building-integrated renewable energy technologies, and IoT-enabled automation, architects can create buildings that are not only more efficient and sustainable but also more resilient to the impacts of natural disasters and other disruptions. Moreover, by integrating smart buildings into larger smart city initiatives, we can create more interconnected, efficient, and livable urban environments for future generations.
Smart Buildings and Robotics

In addition to addressing environmental concerns, smart building technologies, including robotics, offer a plethora of additional benefits that contribute to the overall well-being and productivity of occupants. Robotics, in particular, have emerged as a transformative force in the construction and operation of buildings, revolutionizing traditional construction methods and facility management practices.
One significant advantage of robotics in construction is the ability to automate repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing construction timelines.
Robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors and actuators can perform tasks such as bricklaying, welding, and 3D printing with precision and speed unmatched by human labor. By streamlining the construction process, robotics not only lower costs but also improve safety by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries associated with manual labor.
Furthermore, robotics play a crucial role in facility management, enabling autonomous operation and maintenance of building systems.
Robotic platforms equipped with cameras, sensors, and AI algorithms can autonomously inspect building components, detect defects, and perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, painting, and repair. These robotic solutions not only extend the lifespan of building assets but also minimize disruptions to occupants by conducting maintenance activities outside of regular working hours.
Moreover, robotics hold the potential to enhance accessibility and inclusivity in built environments by assisting individuals with disabilities or mobility impairments. Robotic exoskeletons, for example, can augment the physical capabilities of workers, allowing them to perform tasks that would otherwise be challenging or impossible. Similarly, autonomous robotic vehicles can provide transportation services for individuals with limited mobility, enabling greater independence and participation in social and economic activities.
In addition to their practical applications, robotics in smart buildings also stimulate innovation and drive economic growth by fostering the development of new technologies and industries. As robotics continue to advance, opportunities emerge for interdisciplinary collaboration and cross-sector partnerships, leading to the creation of new jobs, products, and services. By embracing robotics and other emerging technologies, architects and urban planners can not only address the challenges of today but also shape the cities of tomorrow into more efficient, resilient, and inclusive environments for all.
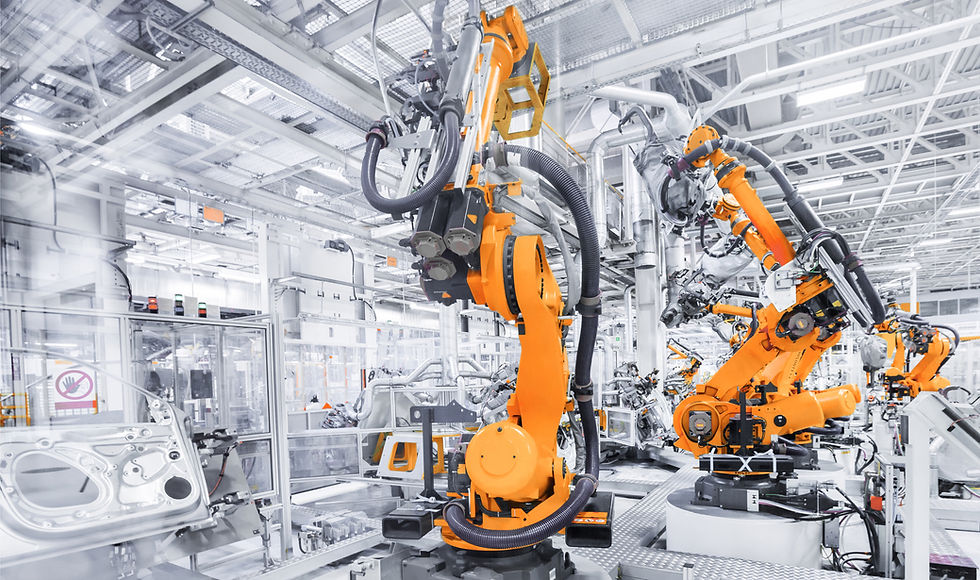
As the demand for sustainable, resilient, and technologically advanced buildings continues to grow, OpDes Architecture stands at the forefront of innovation, pioneering the development of NexGen Smart Buildings that are energy independent and durable.
Through a multidisciplinary approach that integrates cutting-edge technologies, advanced materials, and innovative design principles, OpDes Architecture is redefining the future of building construction and operation. By prioritizing energy efficiency, resilience, and occupant well-being, OpDes Architecture is not only shaping the built environment of today but also laying the foundation for a more sustainable and resilient future. With a commitment to excellence and a vision for a smarter, more sustainable world, OpDes Architecture is leading the way towards a brighter tomorrow.
__________________________________________________________________________________

